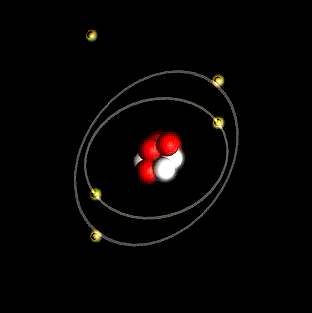
Atoms are the smallest particle that retains the distinctive properties of an element. Atoms are built from even smaller particles, and these particles are like one another, even within other atoms.
Protons have both a weight and a positive unit of charge. Their counter part is an electron which has little weight, but has exactly one negative unit of charge. Neutrons have weight but no charge.
The center of an atom is made up of one or more protons and usually but not always has neutrons. It is called the nucleus. The electrons reside in distant clouds around the nucleus, and are said to orbit the nucleus.
The old model of the atom is shown at the left, and will suffice for our discussions.
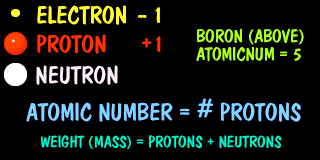
The elements on the periodic table present an orderly listing by their atomic number. The atomic number is simply the number of protons in the element. Each distinct element has the same number of protons, but an element may have a differing numbers of neutrons, and these are called isotopes.
Carbon, for instance, is element 6 (6 protons) but exists in 3 different isotopes. 12C, 13C and 14C. They would be called carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14. They have 6, 7 and 8 neutrons respectively.
The actual atomic weight of carbon is calculated by adding the per centages of each isotopes weight. Carbon has an average mass of 12.011.
Electrons maintain a very orderly structure based on their energy. Most chemical reactions ( between two or more different elements) occur because electrons want to be moved or shared between atoms. Electrons like to exist in pairs, they are less happy (energetically speaking) to exist by themselves.
An element can give up an electron if the loss creates a more stable electronic configuration and there is another element willing to accept it. When an element accepts or gives up an electron it becomes charged and is called an ion.
For example, if the element sodium give up its lone exterior electron it creates a stable electronic structure and becomes positively charged, it is then a cation. If the element chlorine accepts the electron, it then has a stable outer shell and becomes negatively charged. A negatively charged element is called an anion.
When sodium and chlorine react to form a compound they become a ion pair and make the new compound sodium chloride. It has no net charge as the two ions balance each other. This type of bonding is called "ionic". When one atom gives up all of its unpaired electrons and another accepts them, none are being shared between the two, and the bond is called ionic.
|
electron shells |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
max electrons |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
electron shells: |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
| elemental |
Sodium |
|
|
|
|
|
||
| elemental |
Chlorine |
|
|
|
|
|
||
| ionic |
Sodium +1 |
|
|
|
|
|||
| ionic |
Chloride -1 |
|
|
|
|
6 |
|---|
A molecules is created when two or more atoms come together to form a material with new properties, and no net charge. Compounds (molecules) have fixed ratios of atoms .
A molecule is the smallest structural entity that describes the distinctive properties of the material. The forces which hold molecules together is called bonding.
Ionic bonds are weak bonds. They are formed by unlike charges attracting. Ionic bonding happens when one atom gives up its electrons to another and they are not shared.
Notice in the above table, when sodium gives up one of its electrons (the single one in the outer most shell) (1) to chlorine, both atoms end up with paired electrons in their outer most shells (2 and 6) so both have achieved stability. Sodium and chlorine exchange the electrons and become the sodium and chloride ions.
The resultant compound is sodium chloride (table salt), and the mineral name is halite.
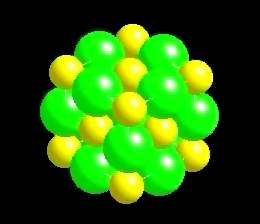
Halite
NaCl
|
Na |
+1 |
Cl |
-1 |
|
| NEXT | TOC | PREV |